Starting methods of synchronous motor
A synchronous motor is an AC electric motor that always rotates at a synchronous speed. This speed is achieved with the help of the rotating magnetic field produced by the stator winding. It depends on the supply frequency and the number of poles in the motor.(Ns = 120f/P).
The torque produced by the motor is a pulsating torque, but not the rotating torque. It is because of the large inertia of the rotor and continuous magnetic reversal of the stator field. Hence the motor could not able to start. It is important to understand the working of synchronous motor.
In order to create a rotating torque, and make the motor rotate at synchronous speed, some external means must be used. Using any one of the starting methods of synchronous motor, it should be rotated near to the synchronous speed.
Methods of starting
By means of Pony motor
In this method of starting, a small induction motor(called a pony motor) is coupled to the rotating shaft of the synchronous motor. The induction motor should have less number of poles than the synchronous motor so that speed near to the synchronous speed can be achieved.
The three-phase supply is given to the synchronous motor, which creates the rotating magnetic field. Now supply is given to the induction motor, which starts to rotate.
When it rotates the rotor of the synchronous motor near to the synchronous speed, the DC switch of the main synchronous motor is closed. Doing this, will pull the motor into synchronism and starts rotating at synchronous speed.
Once the synchronism is established, there is no need for the induction motor, hence it is decoupled.
By means of dc machine
The method of starting synchronous motor using a dc machine is similar to the previous method. Instead of the induction motor, a dc machine is coupled to the rotor shaft of the synchronous motor.
At first, the dc machine is operated as a dc motor to rotate the main motor shaft. The speed of the dc motor is adjusted by the speed regulator. Once the synchronous motor achieves the sub-synchronous speed, it is excited with the dc supply. By doing synchronism is achieved by the motor.
The dc machine acts as a load on the synchronous motor. Now the dc machine can be used to provide dc supply to the rotor winding of the synchronous motor.
By providing damper winding
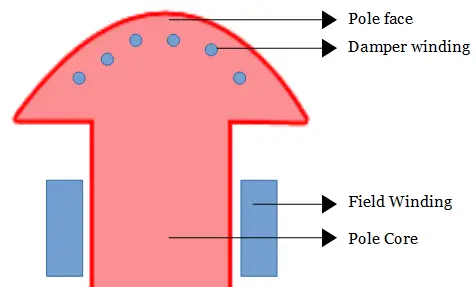
It is one of the most commonly used starting methods of synchronous motor. In this method, the motor is first started as a squirrel cage induction motor by providing an additional winding on the rotor poles, called damper winding.
In the salient pole machine, the winding consists of copper bars, which are placed into the slots provided on the outer periphery of the pole shoes. The ends of the copper bar are short-circuited with the help of end rings, which look like a squirrel cage rotor.
In a non-salient pole machine, the damper winding conductors are placed in the rotor slots above the main field winding and short-circuited by the end rings. The damper winding makes the motor behave as an induction motor.
When the synchronous motor is connected to a 3-phase supply, a rotating magnetic field is set up which causes the rotor to rotate as a squirrel cage induction motor.
As soon as the rotor attains about 75% synchronous speed, the rotor winding is connected to DC mains. At that instant, the rotor field is magnetically locked with the stator rotating field and the motor starts running runs as a synchronous motor.
When the motor attains the synchronous speed, the relative motion between the damper winding and the magnetic field will be zero. Hence no emf is induced in the damper windings anymore and will become inactive.
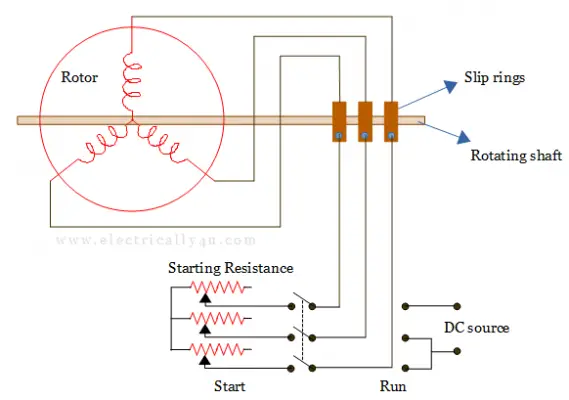
By using slip ring induction motor
In this method, the rotor winding is designed to form a three-phase star or delta-connected winding. The three ends of this winding are brought out through slip rings.
An external rheostat is connected in series with the rotor. So when the stator is excited with the 3phase supply, the motor starts as a slip ring induction motor. Due to the additional resistance in the rotor, it provides high starting torque. As the motor gathers speed, the resistance is then gradually cut off.
When the motor rotates at a speed near the synchronous speed, the d.c. excitation is turned on. The motor gets pulled into synchronism and starts rotating at synchronous speed. The initial resistance added in the rotor not only provides high starting torque but also limits the high inrush of starting current.
At the time of starting, the motor runs as a slip ring induction motor. While running, once the synchronous speed is achieved, it acts as a synchronous motor. If the starting and excitation are done automatically, the motor is known as an auto-synchronous motor.
Among the different starting methods of synchronous motor, the squirrel cage windings are not effective during normal operation, as it has less starting torque. When the motor is operated as a slip ring induction motor, it provides the necessary torque for rotating the motor.
Procedure to start a synchronous motor
A synchronous motor provided with damper winding is started by using the following procedure.
- Reduced voltage is given to the stator terminals of the synchronous motor, with the help of an autotransformer.
- When the motor picks up the speed, the DC excitation to the rotor is turned on. If the excitation is sufficient, then the machine will be pulled into synchronism.
- Now, the rated voltage is applied across the stator terminals by adjusting the autotransformer.

Related Posts